Database And Business Intelegence – We need to carefully analyze sales and click data to make strategic decisions about which products should be featured in our store. One such form of data analysis is business intelligence.
If there is an abundance in the world today, it is data. At the heart of every information system is a database that contains event information. For example, who bought what, when, how much, and so on. It is important to know the architecture of event systems so that data processing is not a complete mystery.
Database And Business Intelegence
However, it is important to know how to filter and analyze the collected data in order to make management decisions. For example, after summarizing thousands of records, we might find a product that sells particularly well with women of a certain age group living in a certain region. This meaningful information can be actionable for supply chain and marketing initiatives.
Mis781 Business Intelligence And Database Assignment
If anything in today’s world, there is probably too much data. Breaking down information into meaningful information is a key skill. There are many tools for data analysis. These include spreadsheet programs such as Excel and database systems such as Access. Learning how to use these tools will increase your marketability.
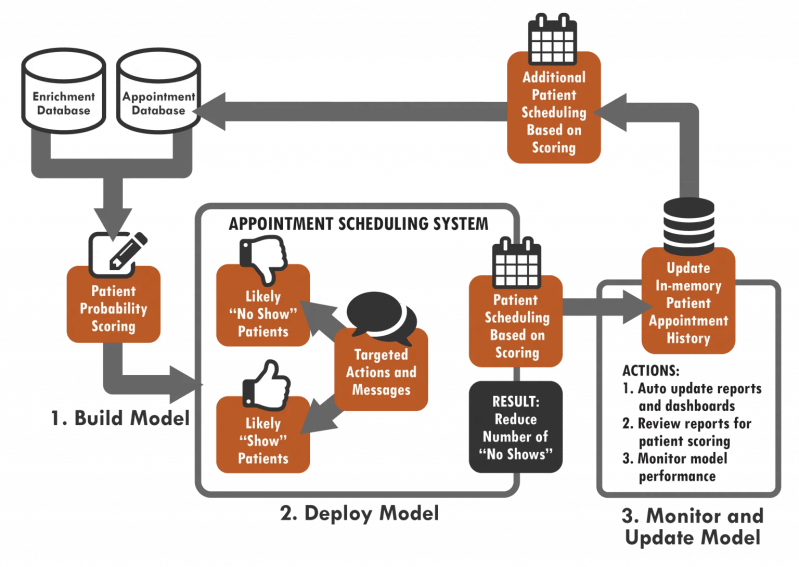
Many information system projects are planned for a life cycle that moves from analysis to implementation. The diagram below shows the steps we will cover in the current chapter:
To demonstrate the power of summary data, we’ll first show how it can be used as a website marketing tool. Impressive statistics help encourage repeat business. The same marketing principles also apply to non-profit organizations.
Kiva is a website that allows you to grant small loans (usually under $500) to entrepreneurs in developing countries. The branch of microfinance, called microfinance, is the granting of very small loans (usually less than $500) to entrepreneurs in developing countries. Most loans are repaid between six months and one year. . Microfinance institutions are an incredibly valuable resource in helping Third World citizens rise out of poverty. Surprisingly, the repayment rate for the world’s poor ranges from 95-98%, which is much higher than the US loan repayment rate. More than 80% of Kiva’s loans go to female entrepreneurs. They invest the profits back into the companies and improve the lives of their families.
What Is Business Intelligence? Bi Definition, Meaning & Example
For example, Kiva combines resources so that 50 people can each borrow $10 for a total of $500. As part of its marketing work, Kiva maintains up-to-date information about its activities. For example, they say they have nearly half a million lenders who have loaned a total of $161 million over the past three years. These fast facts represent business information gathered from the website’s database after scanning millions of records. The data is not only a marketing goal, but also an internal scorecard that monitors the progress of Kiva’s mission and influences decisions.
Kivan’s Facts and history page is a company information report. Note the sentence under “Recent statistics” stating that the statistics are updated at night (between 1 and 3 am). This is typical for business intelligence systems. These operations are usually performed at peak times because searching through millions of records causes such a drain on the system.
A nice example is a type of business intelligence that delivers correct and relevant information to the relevant decision makers in the necessary time to support effective decision making. . Business Intelligence (BI) is the delivery of accurate and relevant information to the relevant decision makers in a timely manner to support effective decision making.
By this definition, all the work we do with Excel is business data because our submissions contain accurate and useful information that helps us make effective decisions. However, he understands that business intelligence involves filtering and analyzing large data sets, such as those in companies’ databases. The subject of this chapter is extracting and analyzing data stored in databases. You may be asked to participate in this type of analysis at various points in your career.
What Is Saas Business Intelligence? Benefits & Usage
Business Intelligence is part of the big picture information system architecture. Most existing systems can be classified as business systems, collaboration systems or business information systems. The company’s systems – for example when taking orders – enter their data into the data warehouse, which in turn is asked to support the company data.
For example, let’s say that our goal is to develop a clothing business that produces high-quality products and keeps costs under control. We measure product quality by determining the percentage of products rejected by inspectors at each location. (Think of the 99 tags you find in the pocket of your new suit. The inspector approves the suit you wear.) A relatively high rejection rate is a red flag to management that requires further analysis. Is this too much of a regulator? Is there a pattern for rejected products? Does one location in the factory tend to reject more than others?
Suppose our analysis determines that the largest rejection comes from only one plant in Southeast Asia. We report the problem to management. They send a team to evaluate the facility. The review reveals child labor, squalid conditions and extremely low morale at the factory. Bad conditions change quickly and the rejection rate returns to the average.
Information system architecture Business Intelligence Division. Business Intelligence systems usually work from a data warehouse – the company’s data warehouse. Every business system contains one or more databases. The content of these databases is routinely copied to the data warehouse to enable BI analytics. The copying process is called Extract, Transform and Load (ETL).
Network Server Of Computers And Business Intelligence.database Security System. Backup Data Traffic Analysis. Big Data And Cloud Computing Banner Conc Stock Vector Image & Art
Static reports are the most familiar form of BI reporting – summary reports are distributed at regular intervals. They are by far the most common types of business information. Most companies include prepackaged and printed standard reports to assist management in decision making. For example, universities use enrollment reports to assess which departments need more faculty. Credit card companies request reports from people with high credit scores so they can target credit card offers. Accordingly, the companies are aimed at university students who have good future earning potential. Marketers can look at the sales figures of different stores and regions to determine if there are opportunities for sales promotion.
Dynamic reports look like regular reports, but there is one big difference. They are interactive and allow the user to search for the source of the summary numbers. Similar to static reports, but online and interactive. The manager is curious about which dashboard has a certain summary number. High-level management overview of information – sometimes displayed using clocks and needles resembling a car dashboard. You may not need to know your exact RPM in the car, but you do need to know if you are red. Similarly, senior management may not need to know exact sales numbers, but they do need to know if sales are outside the normal range. It can reverse the process of identifying numbers that contribute to the generation of the resulting summation number. Digging is like checking your ATM balance and then making a phone call to get a list of withdrawals and payments made to your account. To reveal the details that contributed to the number. It’s basically an information-gathering cycle, with the information gained at each step providing clues as to where to look next. For example, if sales are down in North America, try to figure out what’s happening in the Midwest. Then step forward to find the problem at the Cleveland, Ohio plant.
Data mining The process of using computer power to hunt for patterns in data because you don’t know what to look for. Uses computer programs and statistical analysis to look for unexpected patterns, correlations, trends, and data sets. It basically fishes through the data to see if there are any interesting patterns. A common example of data collection is knowing that you buy beer and diapers often when you go to the grocery store. If they ask more, the marketers find out that dad picks up a few beers on his way to the grocery store to buy diapers. Marketers can use this information to place the two products closer together in the store.
The Business Intelligence process for dynamic reports is shown here. The upper part of the diagram shows how data enters the data warehouse through extraction, transformation, and loading. Dynamic reporting starts with an executive dashboard that provides a high-level view of the business. The dashed red arrows represent an excavation aimed at finding the reason for the pattern in the data. In this example, the decline in North American sales was followed until the end.
Amazon.com: Business Intelligence Career Master Plan: Launch And Advance Your Bi Career With Proven Techniques And Actionable Insights: 9781801077958: Chavez Eduardo, Moncada, Danny: Books
Us business email database, free business contacts database, business listings database, business email database, business to business database, buy business list database, business intelegence, business leads database, small business database software, business contact database, purchase business database, international business database