Corporate Environmental Responsibility (CER) is not just a buzzword; it’s a transformative force reshaping the corporate landscape. This captivating narrative delves into the evolution of CER, its core principles, and the multitude of benefits it offers businesses. We’ll also explore the challenges and opportunities associated with CER implementation, providing insights and strategies for overcoming hurdles. Finally, we’ll examine industry-specific applications and emerging trends, showcasing how CER is shaping a more sustainable future.
From Seed to Stature: The Definition and Evolution of CER
CER refers to the voluntary actions businesses take to minimize their environmental impact and contribute positively to the environment. Its roots trace back to the 1970s, a period marked by growing public awareness of environmental issues. As the understanding of businesses’ significant role in environmental protection deepened, CER emerged as a critical concept.
The Winds of Change: Factors Driving the Importance of CER
Several factors have propelled CER to the forefront of business considerations:
- Consumer Demand: Consumers are increasingly opting for products and services from environmentally conscious companies, making CER a business imperative.
- Regulatory Pressures: Governments worldwide are enacting regulations to curb corporate environmental impact, making CER a legal necessity.
- Investor Interest: Investors are recognizing the financial advantages of CER, with companies demonstrating strong environmental practices often experiencing better financial performance.
- Reputation Management: CER enhances a company’s reputation, fostering customer loyalty and trust.
- Cost Savings: Implementing CER practices can often lead to cost savings through reduced energy consumption, waste minimization, and improved operational efficiency.
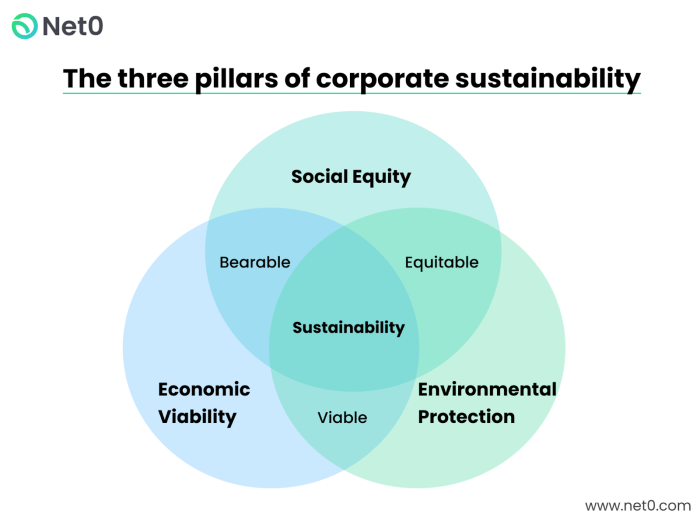
The Three Pillars of CER: A Foundation for Sustainability
CER is a multifaceted approach anchored by three fundamental pillars: environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic sustainability. These pillars are intricately linked, guiding organizations towards responsible and sustainable practices.
-
Environmental Stewardship: Corporations are taking greater responsibility for their environmental impact. This involves exploring various options, such as partnerships with environmental organizations, investments in sustainable technologies, and carbon footprint reduction initiatives. By adopting these measures, businesses not only minimize their negative environmental impact but also enhance their reputation and attract environmentally conscious consumers. Environmental stewardship encompasses the protection and preservation of natural resources, minimizing environmental impact, and promoting biodiversity.
-
Social Responsibility: This pillar focuses on upholding ethical labor practices, fostering diversity and inclusion in the workplace, and contributing to community well-being. Examples include ensuring fair wages and safe working conditions for employees, promoting diversity and inclusion within the organization, and supporting local communities through philanthropic initiatives and volunteerism.
-
Economic Sustainability: This pillar emphasizes long-term financial viability, resource efficiency, and waste minimization. Companies can achieve economic sustainability by investing in research and development to improve resource efficiency, optimizing supply chains for reduced environmental impact, and adopting sustainable packaging solutions to minimize waste.
The Benefits of CER: A Win-Win for Business and the Environment
CER isn’t just good for the planet; it’s good for business too. Studies have shown that companies with strong CER practices enjoy a range of benefits:
- Enhanced Reputation: A positive reputation leads to increased sales, as customers are more likely to choose products and services from companies they trust.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Customers are more likely to stick with companies perceived as environmentally responsible.
- Improved Financial Performance: Strong CER practices are often associated with higher stock prices and lower costs of capital, attracting sustainable and responsible investors.
- Climate Change Litigation and Mitigation: As the effects of climate change become increasingly apparent, CER plays a crucial role in mitigating risks associated with climate change litigation. By integrating sustainability into their operations, companies not only reduce their environmental impact but also demonstrate a commitment to a greener future.
Challenges and Roadblocks: Overcoming Hurdles for Successful CER Implementation
Implementing CER initiatives isn’t without its challenges. Here are some common roadblocks companies may encounter:
- Limited Resources: Financial constraints, time limitations, and a lack of skilled personnel can hinder CER implementation.
- Organizational Resistance: Internal resistance from employees or management who are hesitant to change or perceive CER as an additional burden.
- Unclear Goals: The absence of well-defined CER objectives and metrics makes it difficult to measure progress and demonstrate impact.
- Short-Term Focus: Prioritizing short-term financial gains over long-term environmental benefits can lead to inadequate CER efforts.
- Stakeholder Disengagement: Neglecting to involve stakeholders such as employees, suppliers, and customers in CER initiatives can result in limited buy-in and support.
Overcoming Challenges, Charting a Course for Success
Strategic planning and a commitment to continuous improvement are key to overcoming these challenges. Here are some strategies companies can adopt:
- Secure funding (continued): …internal reallocation. Look for opportunities to streamline operations and redirect resources towards CER initiatives.
- Foster a Culture of Change: Foster a culture of environmental awareness and engagement through employee training and communication programs. This will encourage buy-in and active participation from all levels of the organization.
- Set SMART Goals: Establish clear, Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) CER goals and metrics. This allows companies to track progress, measure impact, and demonstrate their commitment to stakeholders.
- Align with Business Strategy: Ensure CER initiatives align seamlessly with the overall business strategy. This fosters long-term sustainability and integrates environmental considerations into core business practices.
- Engage Stakeholders: Actively engage stakeholders in the planning and implementation process. This can involve collaborating with suppliers to adopt sustainable practices, involving employees in waste reduction initiatives, and working with communities on environmental restoration projects. By fostering stakeholder engagement, companies gain valuable input, build trust, and secure wider support for their CER efforts.
Measuring and Reporting: Demonstrating Commitment and Transparency
Measuring and reporting CER performance is critical for several reasons. It enables businesses to:
- Track progress towards sustainability goals.
- Identify areas for improvement and strategize for further progress.
- Demonstrate their commitment to stakeholders, fostering trust and transparency.
Frameworks and Standards: Navigating the Reporting Landscape
Several frameworks and standards guide businesses in measuring and reporting their CER performance. Here are some prominent ones:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): A widely recognized framework providing comprehensive guidelines for sustainability reporting. GRI standards cover a range of environmental, social, and economic indicators, allowing companies to report on their overall sustainability performance transparently.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): Provides industry-specific sustainability accounting standards, aiding companies in reporting financially material environmental, social, and governance (ESG) information.
- International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC): Focuses on integrated reporting, encouraging companies to combine financial and sustainability information into a cohesive report.
CER Across Industries: Tailoring Solutions for Diverse Challenges
CER is not a one-size-fits-all concept. Its implementation varies across industries, each with its unique set of environmental challenges and opportunities. Let’s explore some industry-specific examples:
-
Manufacturing:
- Reducing Waste and Emissions: Utilizing lean manufacturing techniques to minimize waste and energy consumption.
- Sustainable Supply Chain Management: Partnering with suppliers to ensure ethical sourcing and promote environmentally responsible practices throughout the supply chain.
- Product Lifecycle Assessment: Conducting assessments to understand the environmental impact of products throughout their lifecycle, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. This allows for identification of opportunities for improvement in design, production, and recycling processes.
-
Energy:
- Transitioning to Renewables: Investing in renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon footprint.
- Energy Efficiency Initiatives: Implementing smart grid technologies and promoting energy efficiency programs to reduce overall energy consumption.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Exploring technologies to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions, mitigating their environmental impact.
-
Retail:
- Sustainable Packaging: Adopting eco-friendly packaging materials and reducing plastic waste from packaging and product delivery.
- Responsible Sourcing: Partnering with suppliers who adhere to ethical and sustainable practices in their sourcing and production processes.
- Waste Management: Implementing comprehensive waste management programs to reduce landfill waste, promote recycling and composting initiatives, and encourage responsible waste disposal from consumers.
The Future of CER: A Glimpse into a Sustainable Tomorrow
The future of CER is filled with promising possibilities. Here are some key trends shaping its evolution:
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Companies will increasingly prioritize stakeholder engagement, involving a diverse range of stakeholders in their sustainability initiatives. This collaborative approach fosters transparency, builds trust, and ensures CER programs align with broader societal needs.
-
Technological Innovation: Technology will play a pivotal role in advancing CER practices. Data analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology will empower companies to:
- Monitor and optimize environmental performance.
- Identify areas for improvement in resource efficiency and waste reduction.
- Develop innovative solutions to sustainability challenges.
-
Regulatory Frameworks: Stringent environmental regulations, such as carbon pricing mechanisms and extended producer responsibility schemes, will continue to influence CER practices. These regulations will drive companies to adopt more sustainable practices, further accelerating the transition towards a low-carbon economy.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for a Sustainable Future
CER is a powerful force weaving together environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic prosperity. As we look towards the future, businesses that embrace CER as a core value will be well